Rear Steering Racks: Design, Operating Principle, and Diagnostics

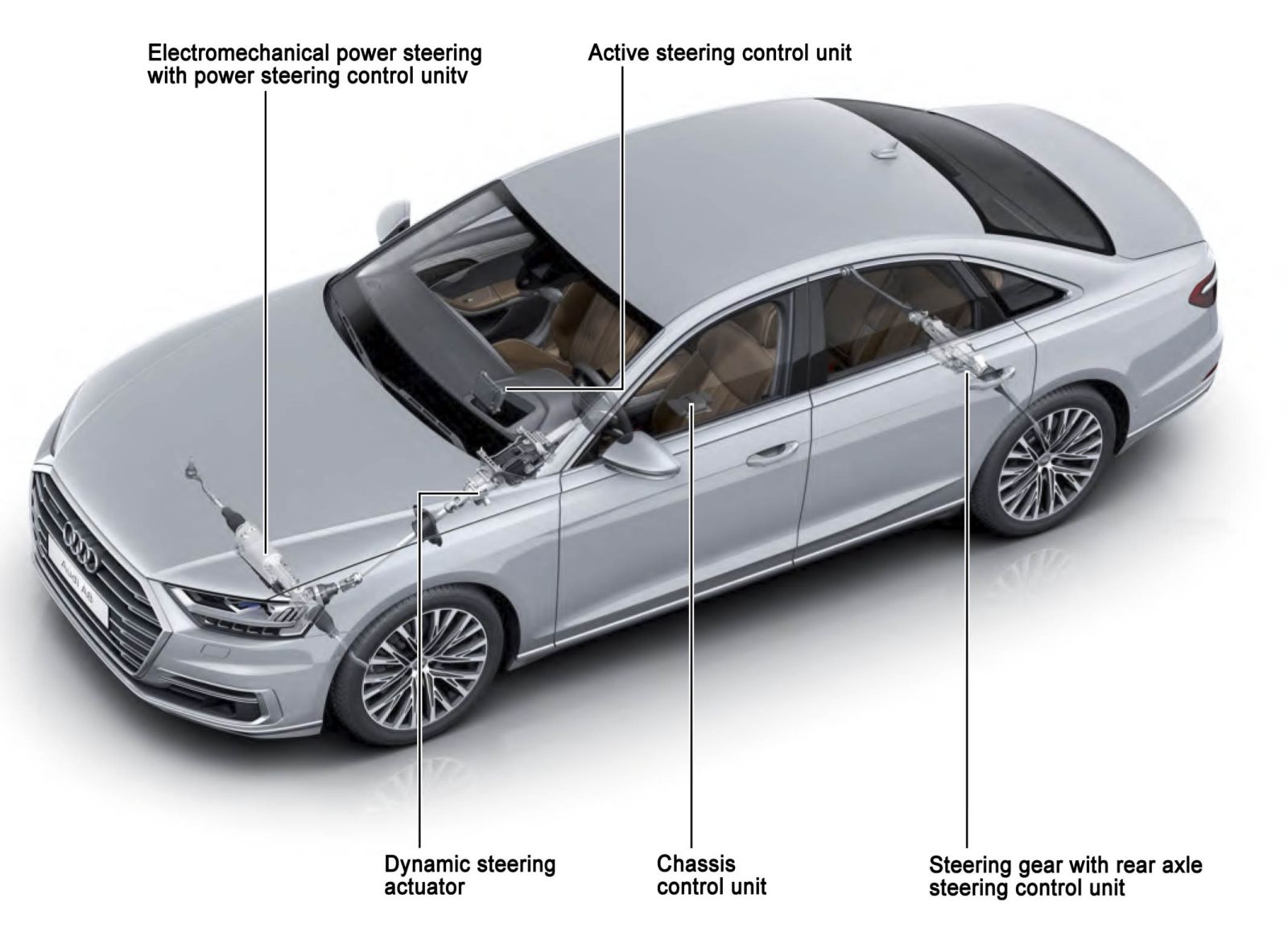
Modern passenger cars and SUVs are increasingly equipped with steering systems with two steerable axles. A key component of such systems is the rear steering rack, which provides active steering of the rear wheels by a small angle relative to the vehicle’s longitudinal axis.
The main functions of the rear steering rack are:
- reducing the turning radius during maneuvering;
- improving directional stability at high speeds;
- enhancing vehicle response during lane changes;
- reducing angular loads on the vehicle body and chassis.
Operating Features of the Rear Steering Rack
The rear steering rack is designed to steer the rear wheels. Unlike conventional steering mechanisms, the rear steering rack has no mechanical connection to the steering wheel. All control actions are generated by an electronic control unit based on data received from various vehicle sensors and systems:
- steering wheel angle sensor;
- wheel speed sensors;
- acceleration and yaw rate sensors;
- ESP stability control system.
Based on this data, the control unit calculates the optimal steering angle for the rear wheels. In certain operating modes, the ESP system may limit or completely block rear-wheel steering if required to stabilize the vehicle in critical situations, such as skidding.
The operation of the rear steering rack is closely integrated with the front steering system, the ESP control unit, and other driving assistance systems. In a two-axle steering system, the rear wheels can steer:
- in counter-phase with the front wheels — at low speeds;
- in phase with the front wheels — at medium and high speeds.
At speeds of up to 50 km/h, the rear wheels turn in the opposite direction to the front wheels. This significantly reduces the turning radius and facilitates parking, U-turns in confined spaces, and urban maneuvering.
At higher speeds, the rear wheels turn in the same direction as the front wheels, but by a small angle. As a result, the vehicle becomes more stable during sudden lane changes, obstacle avoidance, and high-speed driving.
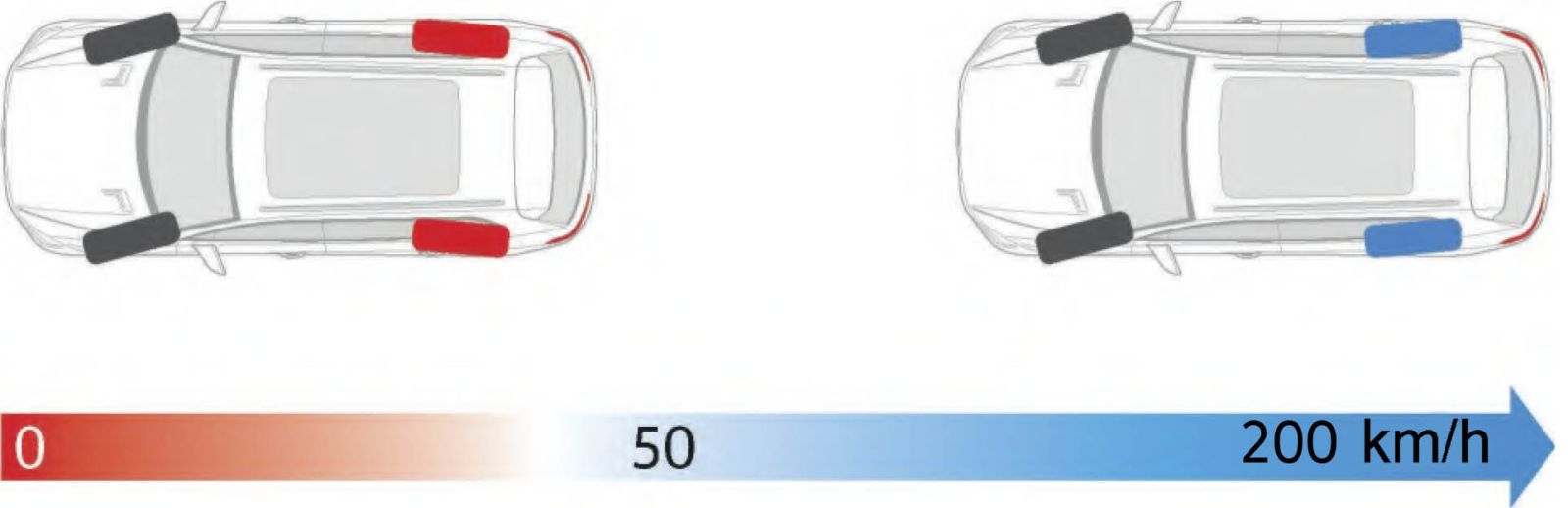

The maximum steering angle of the rear wheels typically does not exceed 2–5 degrees, but even such small values have a noticeable effect on vehicle behavior. Thus, the rear steering rack is part of the vehicle’s integrated active safety architecture and directly affects stability and handling.
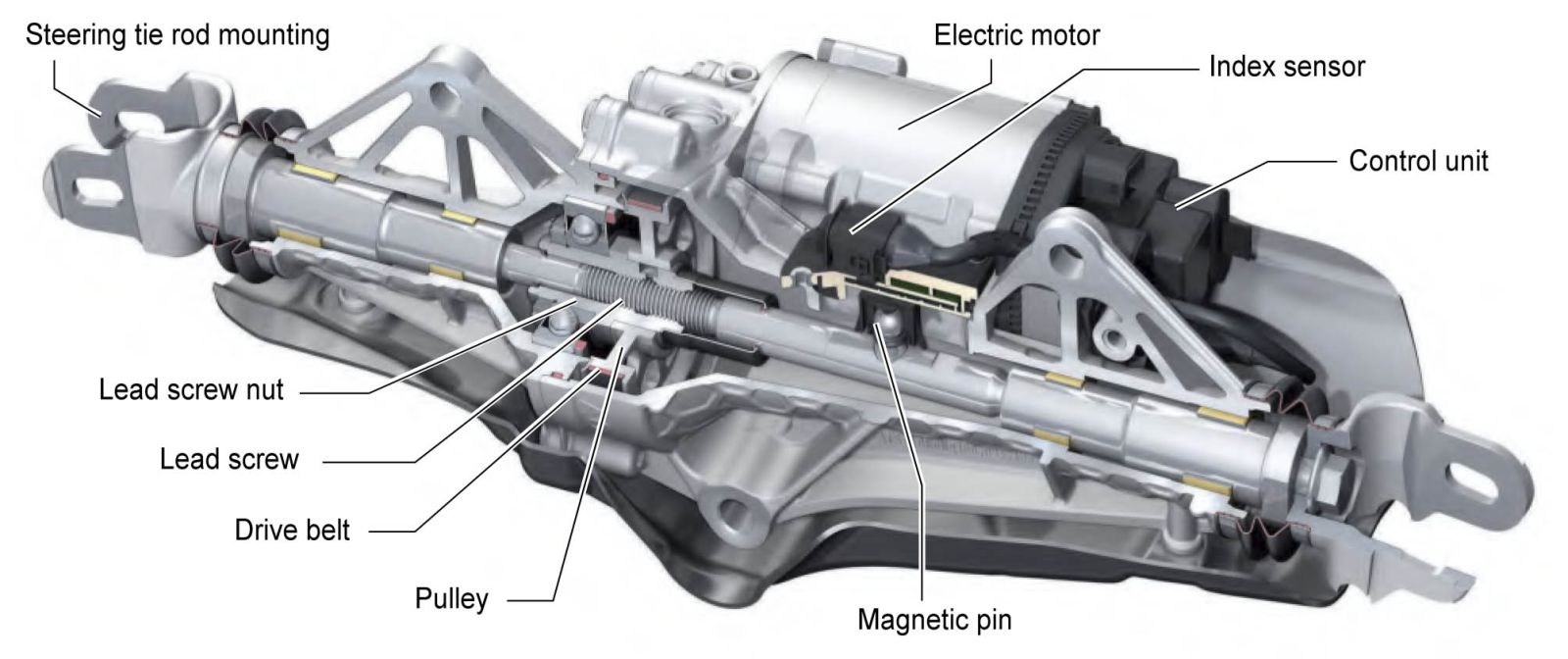
Design of the Rear Steering Rack
From a design perspective, the rear steering rack is a compact electromechanical unit installed on the rear axle of the vehicle. It consists of:
- a rack housing with guides;
- a rack connected to the rear steering knuckles;
- an electric motor (typically brushless);
- a reduction gear (ball screw drive);
- position and steering angle sensors;
- an electronic control unit, usually integrated.
Diagnostics of Rear Steering Actuators Using MS561 PRO
Modern rear steering racks are complex electromechanical units in which the mechanical components are directly linked to electronic control logic. Practical experience shows that most rear steering rack failures are mechanical in nature; however, proper inspection is impossible without electrical activation of the actuator. MS561 PRO is the first diagnostic device that allows rear steering racks to be tested. When power is supplied to the rear steering actuator, the system automatically performs an internal check of the basic position and alignment. This makes it possible to detect:
- assembly errors;
- mechanical defects;
- actuator malfunctions.
Special attention should be paid to vehicles after traffic accidents. In many cases, rear-wheel steering remains inactive until the software is updated. This is particularly common in vehicles of the VAG group, where restoring rear steering rack operation requires reflashing. Currently, this procedure can be performed using a dealer diagnostic scanner or ODIS.
Conclusion
Rear steering racks are becoming an integral component of modern premium-class vehicles. Their diagnostics require a professional approach and specialized equipment. MS561 PRO provides automotive workshops with the capability for accurate diagnostics and servicing of rear steering racks, meeting the requirements of modern vehicles and current repair quality standards.