How do I know if the alternator voltage regulator is in good working order?

The relay controller, despite its compact size, is one of the most important elements of electrical equipment. This key actuator must be in good working order.
PURPOSE OF A RELAY REGULATOR
The relay regulator controls the alternator output voltage, keeping it within certain limits. This ensures proper operation of the vehicle's on-board systems and proper charging of the battery.
.jpg)
Relay controller can have different looks:
- Relay controller in the form of a brush assembly module, uses its structure as a supporting base;
- A separate element mounted on the housing on the support bracket;
.jpg)
The voltage regulator, in any form, is a non-disassembling component. If this component breaks, it cannot be repaired.
SIGNS OF A FALLING RELAY REGULATORA
If a voltage regulator failure occurs, it is accompanied by undercharging or overcharging of the battery, which in turn can be accompanied by:
- complications with starting the engine of the car;
- dull or flickering headlight glow;
- the battery indicator light on the dashboard when the engine is running;
- the battery terminals and battery case are covered with a characteristic white deposit;
- the car may be completely de-energised
Based only on external signs, it is not possible to speak only of a faulty voltage regulator. If the above symptoms appear, a comprehensive alternator diagnosis should be carried out.
The alternator must be checked.
EQUIPMENT for voltage regulator diagnosis
A complete alternator voltage regulator diagnosis can be performed using MSG Equipment.
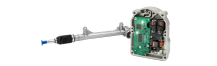
Generator Regulator Diagnostic Equipment
If the diagnosis is done on the car, then you can use one of the testers: MS016, MS015 COM, MS013 COM. The testers allow you to control the alternator voltage regulator, which allows you to detect the presence of abnormalities in its operation. In addition, the testers: MS016 and MS013 COM allow you to test the voltage regulator separately from the generator.
.jpg)
If you are diagnosing an alternator that has been removed from a car, you should use the following stands: MS005, MS008, MS006, MS002, MS004. The bench allows not only to control the voltage regulator, but also to set the load on the generator, simulating real operating conditions. That makes it possible to identify the fault of both the voltage regulator and other parts of the generator.
.jpg)
MSG Equipment develops and manufactures equipment for car dealerships, automotive repair shops and service stations of all sizes. The use of diagnostic devices greatly facilitates the work of the technician, as well as speeds up the repair process of automotive components and units.
EXAMPLE EQUIPMENT LIFE
Seasonality, among other factors, affects equipment payback time. In cold weather, CIG repair is more relevant, in warm weather – less so. An alternative option in the warm season may be the purchase of used starters and alternators, their repair and sale. This will eliminate bench downtime and keep the mechanics busy.
To be more efficient, it is necessary to develop not only the direction of restoration and repair of CYG, but also service stations where you can provide related services:
Starter and alternator rebuilding and repair shop
Personnel - 6 mechanics.
Wage of one mechanic – 30 per cent of the output, the cost of spare parts is not taken into account.
STO (inspection of starters and alternators, repair of starters and alternators, replacement of brushes, retractor relay, replacement of parts of the units)
Staff - 12 mechanics
Wage of one mechanic - 30 per cent of the output
Number of generators per day repaired by one mechanic:
-Mild/Moderate breakdowns – 10-15 units per day (experienced mechanics 20).
Number of generators repaired by one mechanic
- Complex - internal repairs (2-3 units per day.)
Average cost per unit repaired:
Mild/Moderate breakdowns – $15, net profit-$10
Complex - $35, net profit – $20-25
If you are just starting a business and have a limited number of staff, here is a case study of the minimum income at the start of your business as an example.
Case Study
Personnel – 3 mechanics
Performed work for the day:
Repairs (Light/Medium) – 3
Repairs (Complex) – 3
Scheduled Revenue Estimate per Day
|
Minimum "Scheduled" earnings per day of «Sig» |
|||||
|
Service |
Cost of 1 service ($) |
Gross profit of 1 service ($) |
Number of services per day |
Earnings per day ($) |
Gross profit per day ($) |
|
Repairs (Light/Medium) |
15 |
10 |
3 |
45 |
30 |
|
Repairs (Complex) |
35 |
25 |
3 |
105 |
75 |
|
Total amount |
|
|
6 |
$150 |
$105 |
Important! – constant availability of components.