Types of shock absorber diagnostics, main criteria and causes of their failure

A shock absorber – is a mechanism that reduces the level of vertical vibrations of the vehicle and absorbs wheel and body shocks. It is an important element of the vehicle's suspension system.
Varieties, features of the principle of operation
When accelerating, the main load goes to the rear wheels, the car practically on them «squats» when braking, on the contrary, – rear unloaded, and all the emphasis is on the front. During manoeuvres, similar vibrations occur, but already on the sides of the vehicle. It's the shock absorbers that keep your vehicle horizontal, keeping the wheel in the best possible position in relation to the road.
So, quality shock absorbers in your car – this is a guarantee of its safe driving.
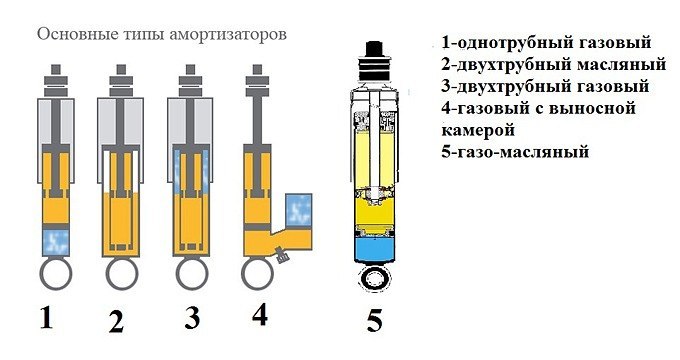
They come in different types: single-tube and double-tube; dry (friction, mechanical), viscous friction (hydraulic) and relaxation; oil, gas and combined; single-acting and double-acting (depending on whether there is resistance on the forward or forward and reverse stroke). Manufacturers usually specify which varieties are suitable for your make of machine.
Main Fault Criteria
The following are signs that there is something wrong with the shock absorbers:
- the car's acceleration changes for the worse;
- decreased load capacity;
- smooth running is replaced by occasional jerks;
- problems with braking (braking distance increases, its trajectory is disturbed);
- the effect of aquaplaning on a wet road surface;
- uncontrollability during driving at speed and in cornering conditions.
In addition to indirect signs of failure, there are a number of ways to diagnose the condition of shock absorbers.
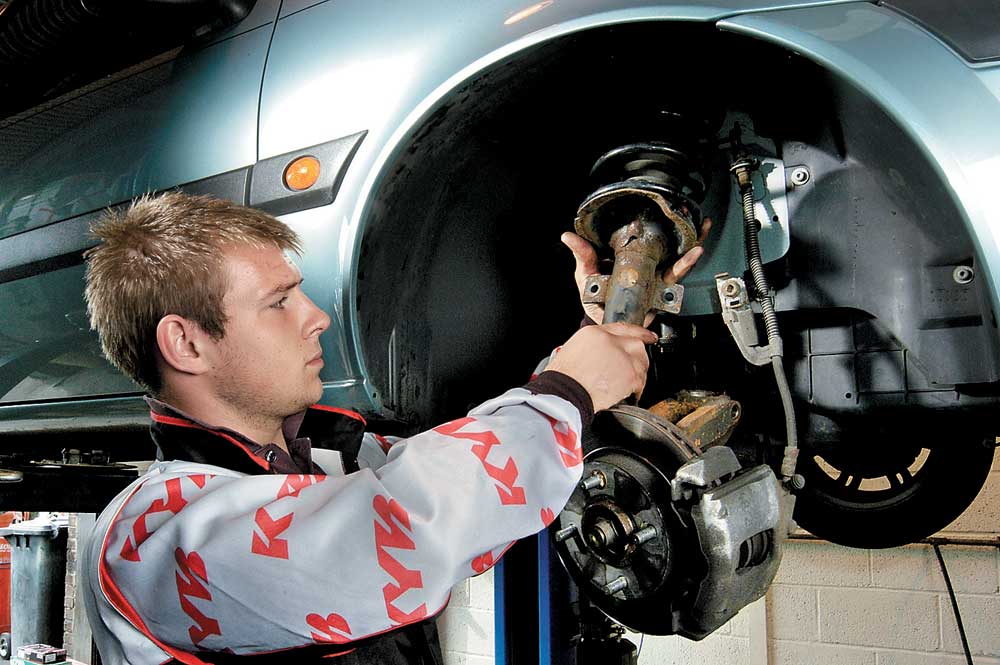

Methods of diagnosis
In the past, malfunctions in this mechanism were determined by rocking the car in different directions several times. After such rocking, the car was released at the lowest point and it had to return to the original position with one return movement. If the rocking continued, and besides there was heard extraneous knocking, then the breakage of shock absorbers was diagnosed. But this method does not always work, stopping can also indicate that the mechanism is jammed. And the modern complex structure of constructions makes this method ineffective.
Direct visual inspection is the second method. Of course, the shock absorber is not in the most favourable place for inspection, but visible oil leaks definitely indicate a malfunction of the mechanism. If there is still any doubt, wipe it off and recheck it a few days later.
A direct visual inspection is the second way.

It's not just the knot itself that can be inspected. If you can see unevenly worn sectors along the side edges of the tyres, this would also be an indication that it's faulty.
See the tyres.
The third method is the in-drive diagnostic technique. To do this, assess the car's handling at a speed of 80 kilometres or more. If it starts rocking, yawing, slow reactions to steering movements – these are all serious indicators that it's time for specialised diagnostics.
And the fourth, most reliable way, – bench, instrumental diagnostics. It is carried out in a service station. The shock absorber is dismantled and placed on the test bench. The damping force is checked at different operating modes. In the case of a vibration test bench, you simply drive your car onto its site. In a relatively short time, qualified mechanics unmistakably diagnose the condition of the shock absorbers and carry out a number of repair or replacement measures.
Main causes of malfunction
Any malfunction of the mechanism is caused by certain reasons. In this case, they are as follows.
- Surface damage or significant scuffing on the chrome coating of the piston rod (due to improper tightening).
- Ageing, wear or overloading of the seal.
- Shock absorber leakage due to worn piston rod seals. This occurs due to ageing, excessive overloading or trivial ingress of dirt or sand.
- Wear of the joints due to ageing or exposure to abrasive materials (sand, dust).
- Inadequate tightening of the bushing (when there is a gap with the upper part of the thread).
- Accident or inaccuracies in assembly (warped stem, broken threads).
Preventive measures
Prevent leaks and shock absorber malfunctions by doing the following. Pay attention as often as possible to the evenness of tread wear and monitor the condition of the bushing. Thoroughly remove all traces from the surface of the assembly after anti-corrosion treatment. Ensure that the housing is not deformed and the stem is not warped. Carry out regular diagnostics, as malfunction of this mechanism will cause malfunctions in the entire suspension system.
The video below shows the process of repairing a Mercedes ML350 (164 body) shock absorber with air suspension. It includes dismantling the shock absorber from the car, diagnostics and repair of the unit on the stand with replacement of defective components with new ones, gas refuelling and installation of the reconditioned unit on the car.
Mercedes ML350 (164 body) with air suspension.
Owing to the use of modern stands for diagnostics and repair of shock absorbers, a workshop specialist can restore a shock absorber of any type and complexity of construction.