MS800 diagnoses lithium-ion battery electric vehicles now
The heart of a car used to be its engine, but now it's the high-voltage battery. The maximum usable power reserve depends on it. All electric vehicles are built around the battery. First electric vehicles used nickel-metal-hydride (Ni-MH) batteries and lithium-ion cells became the standard for electric vehicles a few years later.
What is the service life of a lithium-ion battery of electric vehicles?
The modern high-voltage lithium-ion battery has a complex design and has high durability due to the:
- charge/discharge controller;
- thermal control system;
- the availability of additional reserve capacity to compensate for the loss of capacity over time.
As a rule, electric vehicle manufacturers give an eight-year warranty on the battery and assure you that during this time, the capacity does not fall below 70% of the original. According to Tesla - batteries of their vehicles lose capacity at 2.3% per year, so in eight years the battery will have a capacity of more than 80% of the original.
The presence of a thermoregulation system has the biggest impact on the durability of a high-voltage battery because overheating of the battery cells leads to rapid degradation of its modules. The batteries of early models of electric vehicles and hybrids do not have a thermoregulation system. Budget electric vehicle batteries also do not have. For example, the KIA Soul electric vehicle battery, which has air cooling, suffers from rapid degradation of the upper cells. Batteries without thermal control fail much faster.
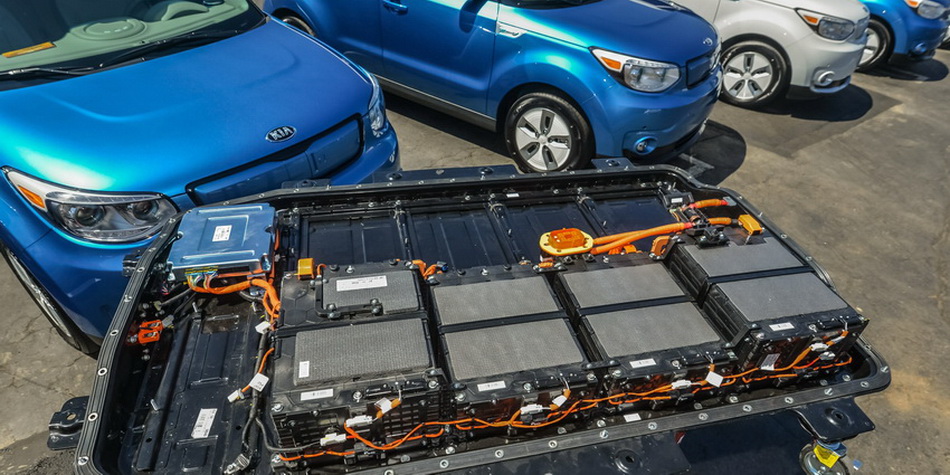

What to do if there are problems with the batteries?
In case of a significant drop in the capacity of the battery, it is not necessary to hurry and change it to a new one. Buying a new battery is very expensive. For a small amount of money, you can check the battery modules and see if it is possible to restore them. In this case, the diagnosis of the battery allows us to determine the capacity of the battery after recovery. Based on the results of the diagnosis, you can make a balanced decision to restore the battery or buy a new one.
Electric vehicle high voltage battery diagnostics
Tester MS800 is developed specifically for the diagnosis of high-voltage batteries of electric vehicles and hybrids. MSG equipment has prepared a tester software update which, along with nickel-metal hydride modules, allows the tester MS800 also check lithium-ion cells. The maximum charge and discharge currents of all module types are 4.5A per charge and 6A per charge. Up to 36 cells can be checked simultaneously. Monitoring the temperature of the modules during the charge/discharge process prevents damage to the modules, being tested during diagnosis.
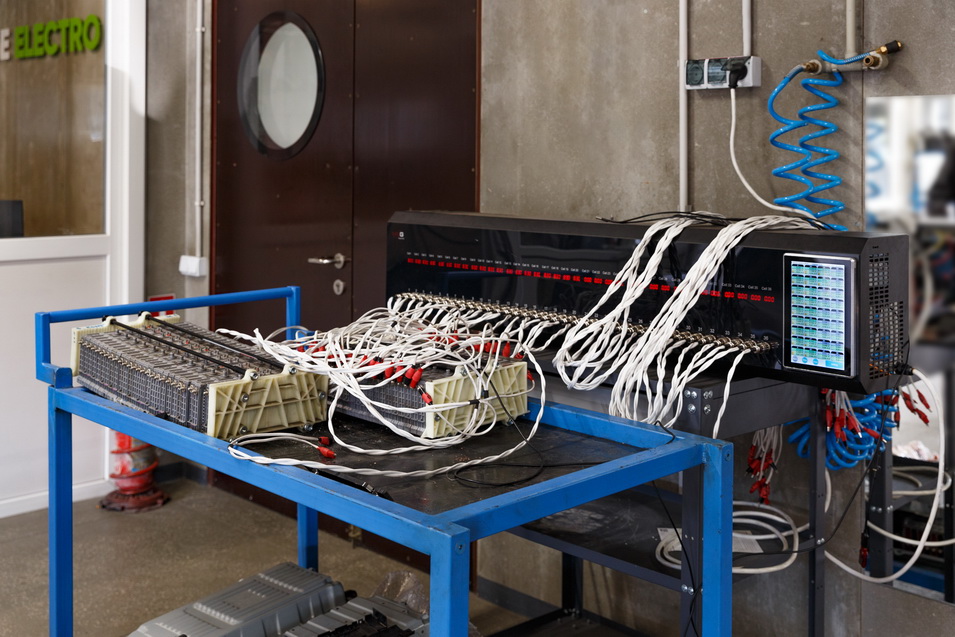

In addition to battery diagnostics, the MS800 allows you to select used cells of similar capacity. Installation of lithium cells in the battery is only possible if all cells have the same voltage. Any cell imbalance reduces the capacity of the collected battery and increases the rate of self-discharge. Too large a difference in voltage between elements from 200 mV or more (different for different models of electric vehicles) can lead to an imbalance error in the BMS module. With the tester MS800, it is possible to balance the cells by charging them or discharging them to a certain voltage with high accuracy.
From the service station, the tester MS800 has another useful function - keeping the cells stored in stock in working condition. Any battery has a self-discharge property. Batteries, which are stored for a long time, should be periodically checked for the charge level and, if necessary, be charged additionally. For lithium batteries, the optimum capacity for long-term storage is between 30 and 60%. Fully discharged batteries are not allowed to be stored, because of the loss of capacity.
For more information about the tester MS800, please write or call: +38 063 745 19 68 (Viber, WhatsApp, Telegram).